![How Long Does Cannabis Stay in Your System? [Tests Explained]](http://marygoroundbongbowl.com/cdn/shop/articles/How_Long_Does_Cannabis_Stay_in_Your_System_Tests_Explained_78a4a71f-3f91-484b-abbd-079a066444b0.webp?v=1756503806)
How Long Does Cannabis Stay in Your System? [Tests Explained]
Posted by Tom Wittneben on
Wondering how long cannabis stays in your system? Whether you’re facing a drug test or just curious about marijuana’s lingering effects, the answer depends on the test type and your habits.
Blood tests might spot THC for up to 7 days, urine tests for up to 30, and hair tests for a whopping 90 days.
Weed often hangs around based on factors like your body fat and how often you use it. Read on to unpack each testing method, what affects retention, and tips to navigate the detox process.
Key Takeaways
-
Cannabis detection times vary significantly across testing methods: blood tests (up to 25 days for chronic users), urine tests (3 to 30 days), saliva tests (up to 3 days), and hair tests (up to 90 days).
-
Factors such as frequency of use, body fat percentage, metabolism, dosage, and potency influence how long THC remains detectable in the body.
-
Employment drug tests for cannabis generally start with an immunoassay screening followed by confirmatory testing, and positive results can lead to legal and employment consequences.
Detection Times by Testing Method
Cannabis can be detected in your body for days to months, depending on the drug test. Each method, whether blood, urine, saliva, or hair has a unique detection window, so knowing these timelines is key if a test is looming.
Here’s the lowdown on each method, breaking down how long THC and its metabolites are typically detectable.
Blood Tests
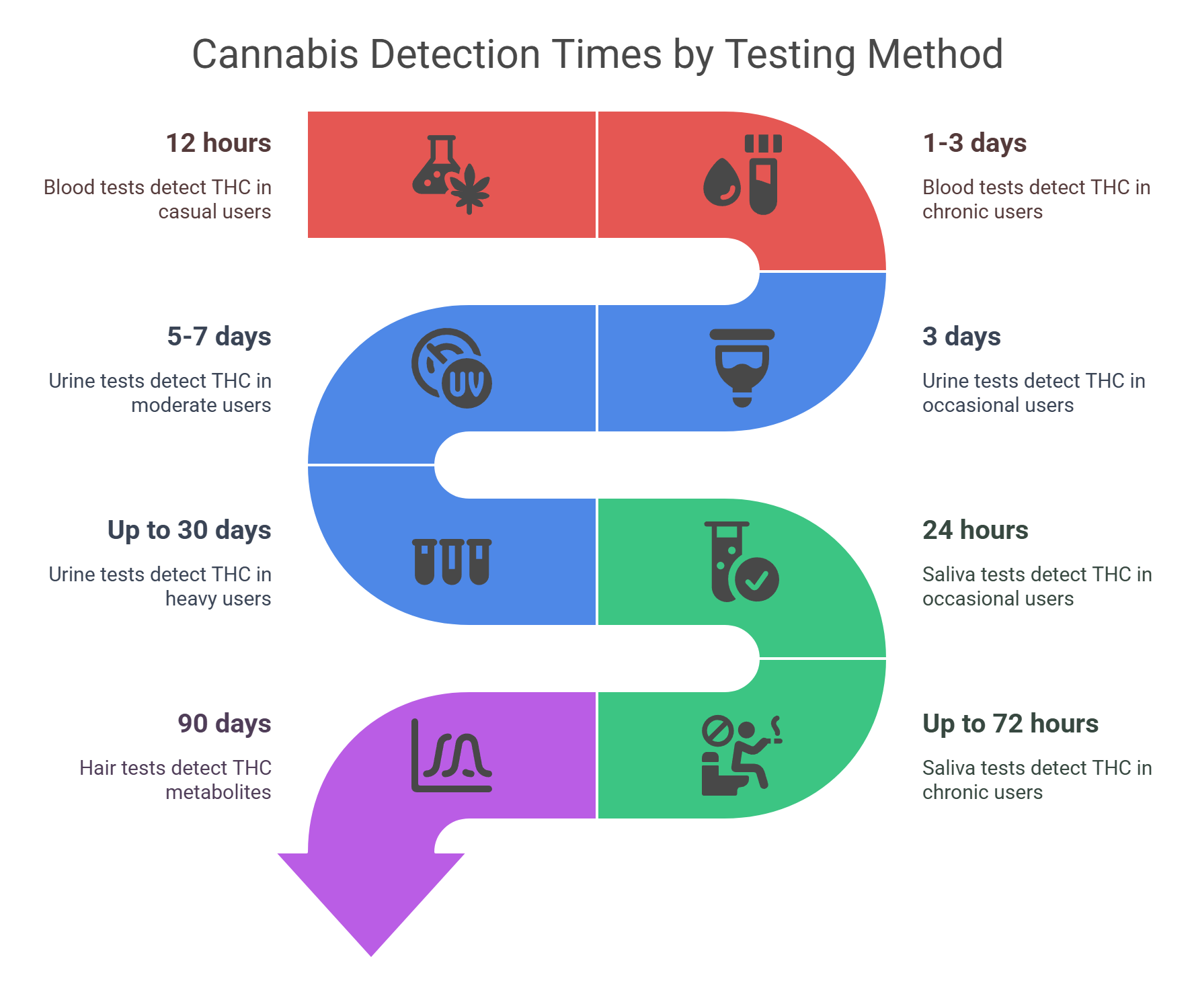
Got a blood test coming up? They often check for recent cannabis use. For casual users, THC is detectable in the bloodstream for about 12 hours, but chronic users might test positive for up to 7 days.
In extreme cases, heavy users can have THC metabolites linger for up to 25 days. This is because the liver breaks down THC, spreading it to tissues like fatty tissues, which slows clearance.
By the way, blood tests are less common for workplace screening but are used in legal cases, like drug driving. They’re great for spotting recent use, typically within 1–3 days. If you’re a one-time user, you’re likely clear after a day or two.
Urine Tests
Urine tests are the most common method for detecting marijuana use, thanks to their low cost and long detection window. They’re the go-to for many employers, making them the most common method for drug screening. How long does weed stay in your urine? It depends on your usage:
-
Heavy users: Up to 30 days or more.
-
Moderate users: 5–7 days.
-
Occasional users: 3 days.
Edibles follow similar timelines, with THC detectable for 3–30 days. Urine tests spot THC metabolites, not active THC, so they catch past use rather than current impairment.
Here’s the deal: Body fat can extend detection in heavy users, as THC loves to hide in fatty tissues. This makes urine tests tricky for chronic users trying to clear a drug test.
Saliva Tests
Worried about a roadside swab? Saliva tests are popular for detecting recent cannabis use, especially in traffic stops or workplace checks.
THC is typically detectable in saliva for up to 3 days. Occasional users might test positive for about 24 hours, while chronic users could show traces for up to 72 hours. In rare cases, detection stretches to 30 hours.
On another note, saliva tests are non-invasive and quick, making them ideal for on-the-spot screening. They focus on active THC, so they’re best for catching use within hours to a couple of days.
They focus on active THC, so they’re best for catching use within hours to a couple of days; learn about THCA vs THC in drug testing and why heated THCA is detected as THC.
Hair Tests
Hair tests are the long-distance runners of drug testing, spotting cannabis use for up to 90 days. They’re often used in workplaces or legal settings to monitor long-term drug use.
THC metabolites get trapped in hair follicles as hair grows, reflecting usage over months. But here’s a catch: second-hand smoke can sometimes cause false positives, making hair tests less reliable.
Guess what? Hair growth rate affects results as faster growth might shorten the detection window slightly. If you’re wondering how long Mary Jane shows up in hair, it’s typically 90 days, regardless of whether you smoked or ate edibles.
Factors Influencing Cannabis Retention
Why does weed stick around longer for some people? Several factors influence how long cannabis and its metabolites stay in your system. From how often you use to your body fat percentage, these variables shape detection times. The exact duration marijuana stays in your system depends on your unique biology and habits.
Let’s look into what keeps THC lingering and how it impacts drug tests.
Frequency of Use
How often you light up (or munch edibles) is a big deal. Frequent use means THC builds up, taking longer to clear. Here’s the breakdown:
-
Heavy users: Over 30 days to clear THC metabolites; chronic heavy users might need 90+ days.
-
Daily users: 30–90 days for complete elimination.
-
Regular users: 30–70 days.
-
Occasional users: 3–15 days.
-
One-time users: 3–7 days.
Chronic users, especially those toking daily, face the longest detection windows, as THC piles up in the body.
Body Fat Percentage and Metabolism
Got a higher body fat percentage? THC loves fatty tissues, creating a “reservoir” that slows clearance. Individuals with higher body fat can retain THC longer, sometimes for weeks after last use. Conversely, a fast metabolism can speed things up, clearing THC quickly.
By the way, genes like CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 also play a role, slowing or speeding THC breakdown. Your overall health, including hydration levels, can tweak how fast your body flushes marijuana.
Dosage and Potency
High-potency cannabis or hefty doses mean longer retention. Stronger strains, like those packed with THC, take longer to leave your system.
For example, a potent edible or high-THC flower can extend detection times compared to low-potency weed. The more THC you consume, the more metabolites your body stores, affecting how long pot stays detectable.
How Does Your Body Process THC?
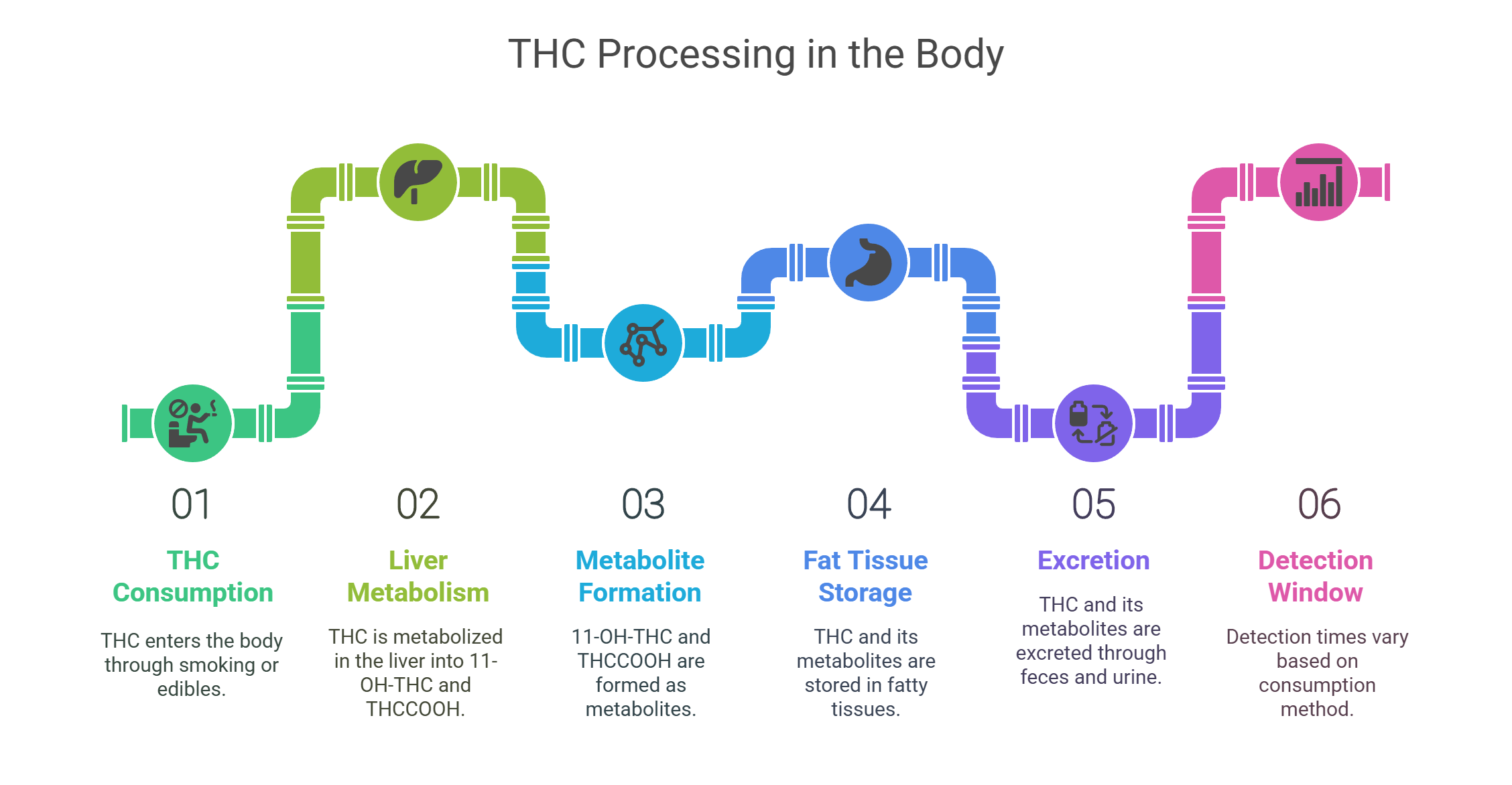
Ever wonder why detection times vary so much? Your body processes THC in unique ways, depending on how you consume it. Smoking hits fast, while edibles linger longer. Understanding this helps explain why drug tests pick up marijuana days or weeks later.
Here’s how THC moves through your system, from metabolism to excretion.
Metabolic Pathways
The liver is THC’s main pit stop. When you consume cannabis, the liver breaks it down like this:
-
THC turns into 11-hydroxy-THC (11-OH-THC), an active metabolite.
-
11-OH-THC becomes THCCOOH, an inactive metabolite that drug tests love to spot.
-
Liver enzymes (cytochrome P450) handle this process.
THC’s lipophilic nature means it sticks to fatty tissues, creating a biphasic elimination pattern; fast at first, then slow as it seeps from fat.
Excretion Routes
How does THC leave your body? Mostly through feces (65–80%) and urine (20–35%). This process can take several weeks, especially for chronic users. The substance’s slow release from fatty tissues is why drug tests catch marijuana long after its effects fade.
Speaking of which, hydration levels and exercise can support excretion, but don’t expect miracles. THC’s exit is a marathon, not a sprint.
Edibles vs. Smoking: Different Detection Windows
The way you consume cannabis changes how long it’s detectable. Edibles and smoking have different timelines due to how THC enters your bloodstream.
-
Edibles: THC from edibles takes longer to metabolize, as it passes through the digestive system. The slow digestion process means more metabolites build up.
-
Smoking/Vaping: THC hits the bloodstream fast via the lungs, leading to quicker detection but shorter retention.
The method of consuming cannabis shapes how long it’s detectable, so choose wisely if a drug test is near.
Healthy Detox Tips
Can you speed up the detox process? Marijuana can take 5–65 days to fully clear, depending on metabolism, body fat, and usage. The most reliable way to pass a drug test is to stop using cannabis. But there are healthy practices to support your body’s natural detox, even if quick fixes are mostly myths.
Here’s what works, what doesn’t, and how to approach detox.
Myths and Realities
Heard you can chug water to beat a drug test. Myth alert: excessive water might dilute urine, but labs catch this, and it won’t clear THC.
Detox kits promising instant results often lack science and can’t outpace your body’s natural process. In reality, THC elimination takes days to weeks, depending on factors like body fat and frequency of use.
For instance, no product can magically flush marijuana in 24 hours. Healthy habits, like staying hydrated and exercising, support detox over time, not overnight.
Healthy Practices
Want to help your body clear THC? Try these evidence-based tips:
-
Stay hydrated: Proper hydration levels aid kidney function, helping flush metabolites via urine. Avoid overdoing it before a test to prevent dilution flags.
-
Exercise regularly: Boosts metabolism, burning fat where THC hides. But skip intense workouts 24–48 hours before a test, as they can release stored THC.
-
Eat well: A balanced diet supports overall health, aiding natural detox.
These habits won’t work miracles, but they help your body process marijuana more efficiently.
Long-Term Effects and Health Implications
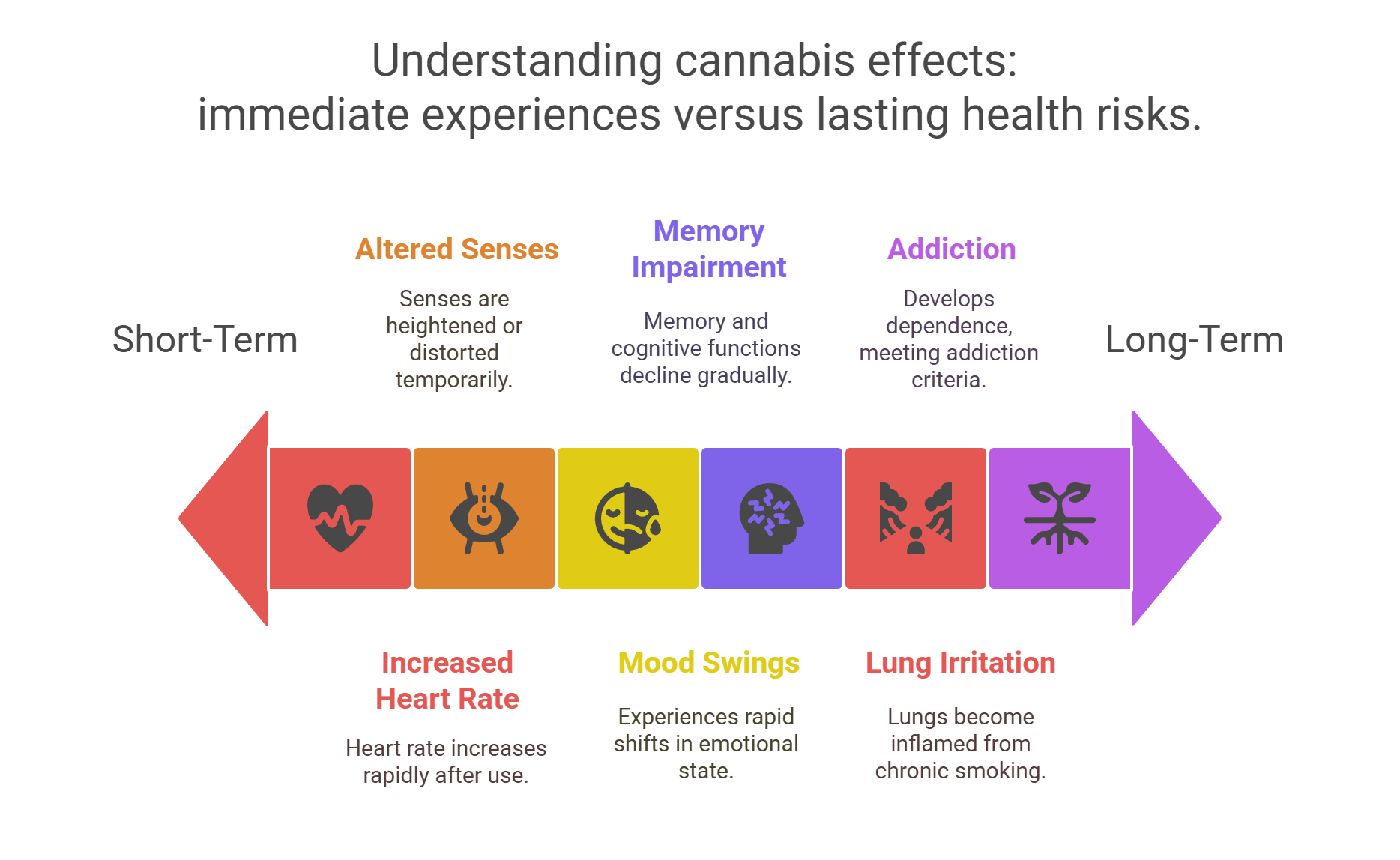
Cannabis isn’t just about detection times. It also has short and long-term health impacts. About 50% of Americans have tried marijuana, often called dope or Mary Jane, but what does it do to your body? From increased heart rate to cognitive risks, understanding these effects is key for mindful use.
Let’s explore the immediate and lasting impacts of cannabis.
Short-Term Effects
Right after using cannabis, you might notice a racing heart or altered senses. Short-term effects include increased heart rate, red eyes, dry mouth, and impaired motor skills.
Mood swings, from euphoria to anxiety, can hit fast, affecting tasks like driving or working. These effects, tied to THC, fade within hours but can impact drug test outcomes if tested soon after use.
Long-Term Health Risks
Long-term cannabis use carries bigger risks. Around 10% of users develop cannabis use disorder, and 30% of current users meet addiction criteria, according to research.
Chronic use can impair memory, attention, and learning, especially in heavy users. Lungs may also take a hit from smoking, increasing irritation risks.
On the flip side, mindful use and breaks can reduce these risks. Knowing the stakes helps you weigh cannabis’s pros and cons.
Will Cannabis Show Up on an Employment Drug Test?
Job on the line? Many employers test for cannabis, even in states where it’s legal. Workplace drug tests often start with an immunoassay screening, followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GCMS) for confirmation.
Here’s what you need to know about employment screening and legal risks.
Common Testing Methods
Most workplace tests rely on urine, the most common method for detecting marijuana. Initial immunoassay screenings catch THC metabolites, with positive results confirmed by GCMS for accuracy.
Saliva tests, used in some workplaces, detect recent use (24–72 hours). Hair tests, though rare, cover 90 days. These methods ensure reliable results, making it tough to dodge detection.
Legal Implications
Testing positive for cannabis can sting. You could face job loss, loss of professional licenses, or legal issues in sensitive fields.
Even hemp products, with trace THC, can trigger false positives, as low levels build up in fat cells. In legalized states, employers still have the right to enforce drug-free policies, so know your workplace rules.
Summary
So far, we have seen that how long marijuana stays in your system depends on the test, your body, and your habits.
As earlier discussed, blood tests catch THC for 1–7 days, urine tests for 3–30 days, saliva for 24–72 hours, and hair for up to 90 days. Factors like body fat, metabolism, and potency play huge roles in how long weed lingers.
Healthy habits like hydration and exercise can support detox, but stopping use is the surest way to pass a drug test. With risks like addiction or job loss, mindful cannabis use is key.
Want to make smarter choices?
Visit Mary Go Round for Expert Guidance
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does THC stay in the system of casual users?
THC generally remains in the system of casual users for approximately 3 to 15 days after consumption. This timeframe depends on various factors, including individual metabolism and frequency of use.
Can consuming hemp lead to a false positive result for THC in drug tests?
Consuming hemp can indeed result in a false positive for THC on drug tests, as low levels of THC may accumulate in the body's fat cells. This emphasizes the importance of understanding the source and content of hemp products.
What is the detection time for THC from edibles in hair tests?
THC from edibles can be detected in hair tests for up to 90 days after consumption. Therefore, users should be aware of the potential for prolonged detection.
How does body fat percentage influence THC retention?
Higher body fat percentages influence THC retention, as THC's lipophilic nature allows it to accumulate in adipose tissue, resulting in prolonged retention. Consequently, individuals with higher body fat may experience longer-lasting effects from THC.
What are the primary routes of THC excretion?
THC is primarily excreted through feces, accounting for approximately 65-80% of excretion, while urine contributes around 20-35%.