Is THCa The Same As THC? Learn the Key Differences
Posted by Tom Wittneben on
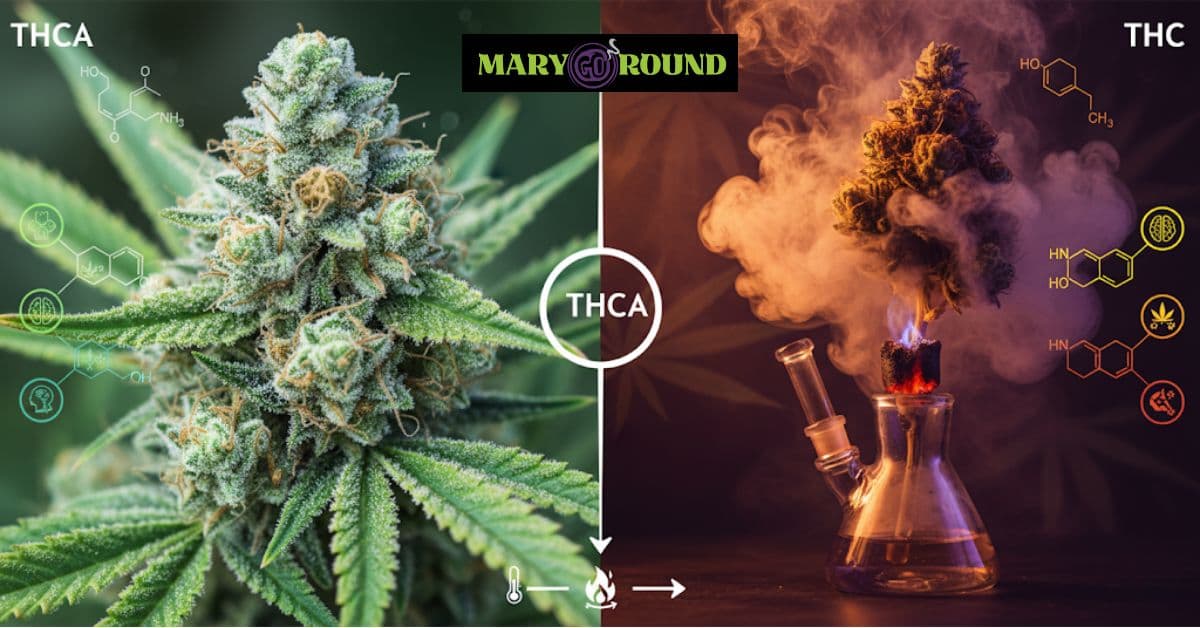
Same plant, different vibes. THCA lives in raw cannabis and keeps things calm. THC shows up after heat and brings the psychoactive effects.
They may sound alike, but THCA and THC play very different roles in the cannabis plant. If you’ve been eyeing THCA flower, curious about its psychoactive properties, or wondering, “Is THCA legal?” you’re in the right place.
Here at Mary Go Round, we’re breaking down THCA and THC so you can roll smarter.
THCA vs THC: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to the cannabis plant, THCA and THC may look similar on paper, but the way they act in your body is completely different. Whether you are consuming cannabis for wellness or recreation, understanding how these two compounds compare can help you get the experience you are actually looking for.
Here is a quick snapshot of how THCA and THC stack up:
|
Feature |
THCA |
THC |
|
Full Name |
Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid |
Tetrahydrocannabinol |
|
Found In |
Raw cannabis, fresh cannabis flower |
Heated cannabis such as smoked, vaped, or baked flower |
|
Psychoactive? |
No. It is a non psychoactive compound |
Yes. It is the psychoactive component responsible for euphoric effects |
|
How It Works |
Interacts weakly with cannabinoid receptors like CB1 and CB2 |
Binds strongly to CB1 receptors in the brain |
|
Activation Method |
Converts to THC through heat, a process called decarboxylation |
Already active once THCA is heated |
|
Potential Benefits |
Anti inflammatory, neuroprotective, immune support, no high |
Pain relief, appetite stimulation, mood support |
|
Best For |
Consuming raw cannabis for wellness without intoxication |
Recreational use and symptom relief that involves psychoactive effects |
|
Legal Status |
Thca legal in some areas, depending on source and risk of conversion |
Considered a controlled substance in many places unless permitted |
|
Drug Test Risk |
Possible if product contains trace THC or has been heated |
Likely, since THC metabolites are commonly detected in tests |
So, What Does This All Mean?
The most significant difference between these two cannabinoids is how they interact with your body and brain. THCA is non psychoactive and found in raw cannabis. It offers potential therapeutic benefits without producing intoxicating effects. THC, on the other hand, is the compound that causes a high. It has strong activity at cannabinoid receptors and is widely used in both medical and recreational cannabis products.
To understand the full picture, keep reading!
Where THCA and THC Come From
To understand the difference between thca and thc, it helps to start with the plant itself.
The Role of the Cannabis Plant
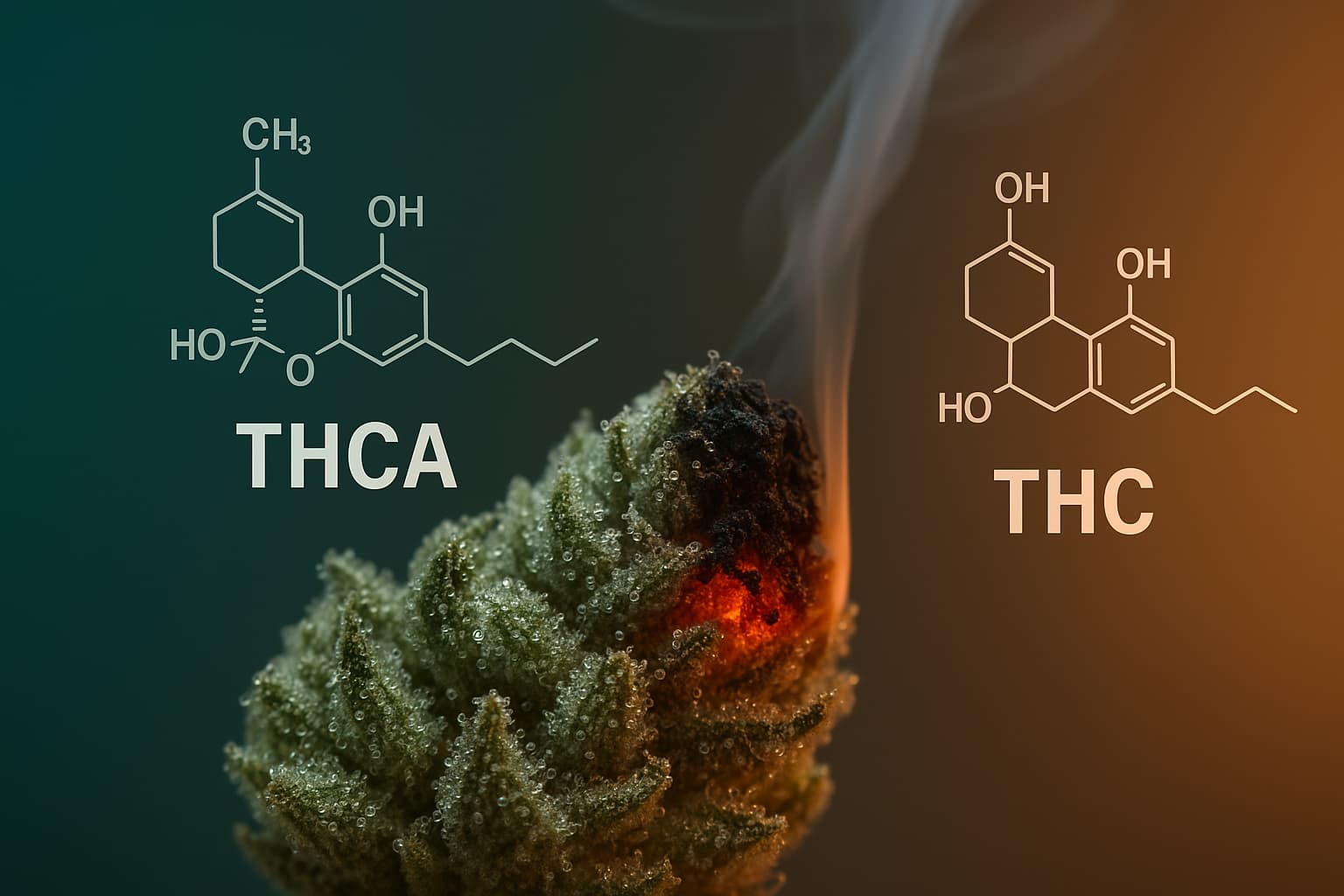
The cannabis plant naturally produces a variety of compounds called cannabinoids. Among them are THCA and THC, along with others like CBD, CBN, and CBG. THCA is the original form produced by the plant. It’s the precursor to THC, meaning the plant first produces THCA, which can later become THC under certain conditions.
This chemical pathway is part of the plant’s natural defense system and evolutionary development. As cannabis strains grow, they produce thca molecules as part of their resin production.
Raw Cannabis and the Natural State of THCA
In its raw form, the marijuana plant is packed with THCA. This means when you consume raw cannabis or fresh cannabis flower, you're mostly taking in THCA, not THC. THCA is a non psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw cannabis buds, meaning it will not cause intoxicating effects unless it's altered.
This makes thca flower ideal for people looking for potential therapeutic benefits without the high. Raw cannabis is even consumed as a raw food supplement by some users, who believe in its potential health benefits.
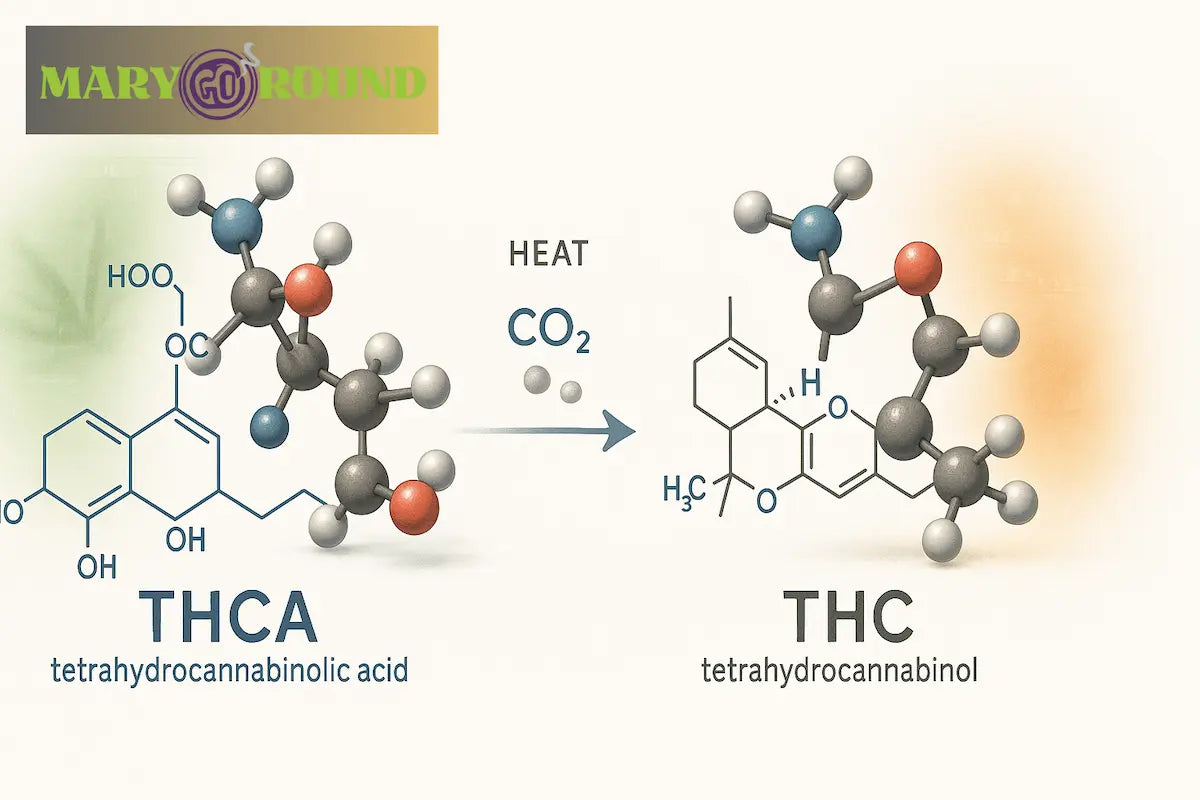
How THCA Becomes THC (Decarboxylation)
So, how do you get from THCA to THC? The answer lies in a chemical reaction called decarboxylation. When you apply heat to cannabis (by smoking, vaping, or baking), THCA undergoes decarboxylation—a process where a carboxyl group is removed from its chemical structure. This reaction converts thca into thc, activating its psychoactive properties.
This is why cannabis use by smoking or vaping leads to psychoactive effects, while consuming raw cannabis typically does not.
According to studies, decarboxylation is the key mechanism that explains why raw cannabis lacks psychoactive effects until heat is applied.
Psychoactive Effects and Properties
Now let’s talk about the effects. For many, that’s the reason they reach for the plant in the first place.
What is THC?
THC (Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis. It’s what causes the euphoric effects or "high" most people associate with marijuana. THC binds strongly to CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which are part of the endocannabinoid system that regulates mood, memory, pain, and more.
When someone consumes cannabis flower through heat, THC activates those receptors and produces psychoactive effects like altered perception, relaxation, and increased appetite.
Recent research confirms THC’s strong activity at CB1 receptors and its use in pain, appetite stimulation, and mood support.
What is THCA?
THCA (Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is the non-psychoactive precursor of THC. It exists in raw cannabis and does not bind effectively to cannabinoid receptors like THC does. This is why THCA does not produce intoxicating effects.
Unlike THC, THCA has a larger chemical structure due to the carboxyl group, preventing it from crossing the blood-brain barrier efficiently. THCA is considered a non psychoactive compound, though it still interacts with other receptors in the body, such as PPARγ (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma), which play a role in inflammation and metabolism.
A 2017 study showed that THCA binds weakly to CB1 and CB2 receptors, confirming its limited psychoactive properties.
Are THCA and THC the Same?
Not at all. The difference between thca and thc comes down to how they interact with your body.
-
THC is a psychoactive compound that causes a high. It binds directly to CB1 receptors in the brain.
-
THCA is a non psychoactive cannabinoid. It only becomes THC through heat. It does not produce psychoactive effects.
That’s the most significant difference: one will get you high, and one will not.
Health Benefits: THCA vs THC
Let’s look at the potential therapeutic benefits of each cannabinoid.
Benefits of THCA
THCA has caught attention in recent cannabis research for offering potential health benefits without the intoxicating effects.
-
Anti Inflammatory: THCA activates PPARγ, reducing inflammation in models of arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
-
Neuroprotective Effects: Studies show THCA may help protect brain function and slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
-
Anti Nausea Properties: THCA has reduced nausea and vomiting in animal models.
-
Non Psychoactive Benefits: Because it is a non psychoactive cannabinoid, it can be used during the day without altering cognition.
-
Immune System Support: Preliminary data suggests THCA may modulate immune response and help regulate immune-related conditions.
-
Potential Therapeutic Properties: Early lab research supports its role in treating inflammation, obesity, and diabetes.
Benefits of THC
THC has been studied more extensively due to its long-standing use in medical or recreational use.
-
Pain Management: THC is effective in reducing chronic pain, especially in patients with nerve damage or cancer.
-
Appetite Stimulation: Known for "the munchies," THC can stimulate appetite, which helps patients dealing with appetite loss.
-
Mood Support: THC may offer stress relief and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression in moderate doses.
-
Anti Inflammatory: Like THCA, THC also interacts with immune cells to reduce inflammation.
-
Anti Nausea Effects: THC is approved in several countries as a treatment for chemotherapy-related nausea.
How People Use THCA and THC
Understanding how THCA and THC are consumed can help cannabis enthusiasts choose the best method for their lifestyle, goals, and tolerance. The method of use influences whether you experience psychoactive effects, how your body absorbs cannabinoids, and how long the effects last.
Consumption Methods
The way you consume cannabis determines whether you activate THC or preserve THCA.
To consume THCA:
-
Juice raw cannabis or blend raw cannabis buds into smoothies
-
Use cold-processed tinctures or topicals that preserve the raw chemical composition
-
Take capsules that list tetrahydrocannabinolic acid as the active ingredient
-
Use THCA products labeled as non-decarboxylated
To create THC:
-
Apply heat through smoking, vaping, or baking
-
This chemical reaction causes THCA to convert to THC
-
Heating activates the psychoactive compound that binds to brain receptors
Whether you are dealing with chronic pain or exploring cannabis for neurodegenerative diseases, your method of consumption plays a big role in results.
Product Types and Forms
THCA and THC are available in a range of product formats. Here is how they differ:
THCA Products:
-
THCA Flower: Sold for juicing or for smoking. If heated, it will convert to THC
-
Raw Edibles: Infused with THCA but not heated, keeping it non psychoactive
-
Cold-Processed Tinctures: Designed to preserve THCA molecules
-
Topicals and Capsules: Used as part of wellness or dietary supplement routines
THC Products:
-
Edibles and Gummies: Pre-activated with THC through decarboxylation
-
Vape Carts and Oils: Contain active THC ready for immediate effect
-
Concentrates: Potent options for experienced cannabis consumers with high tolerance
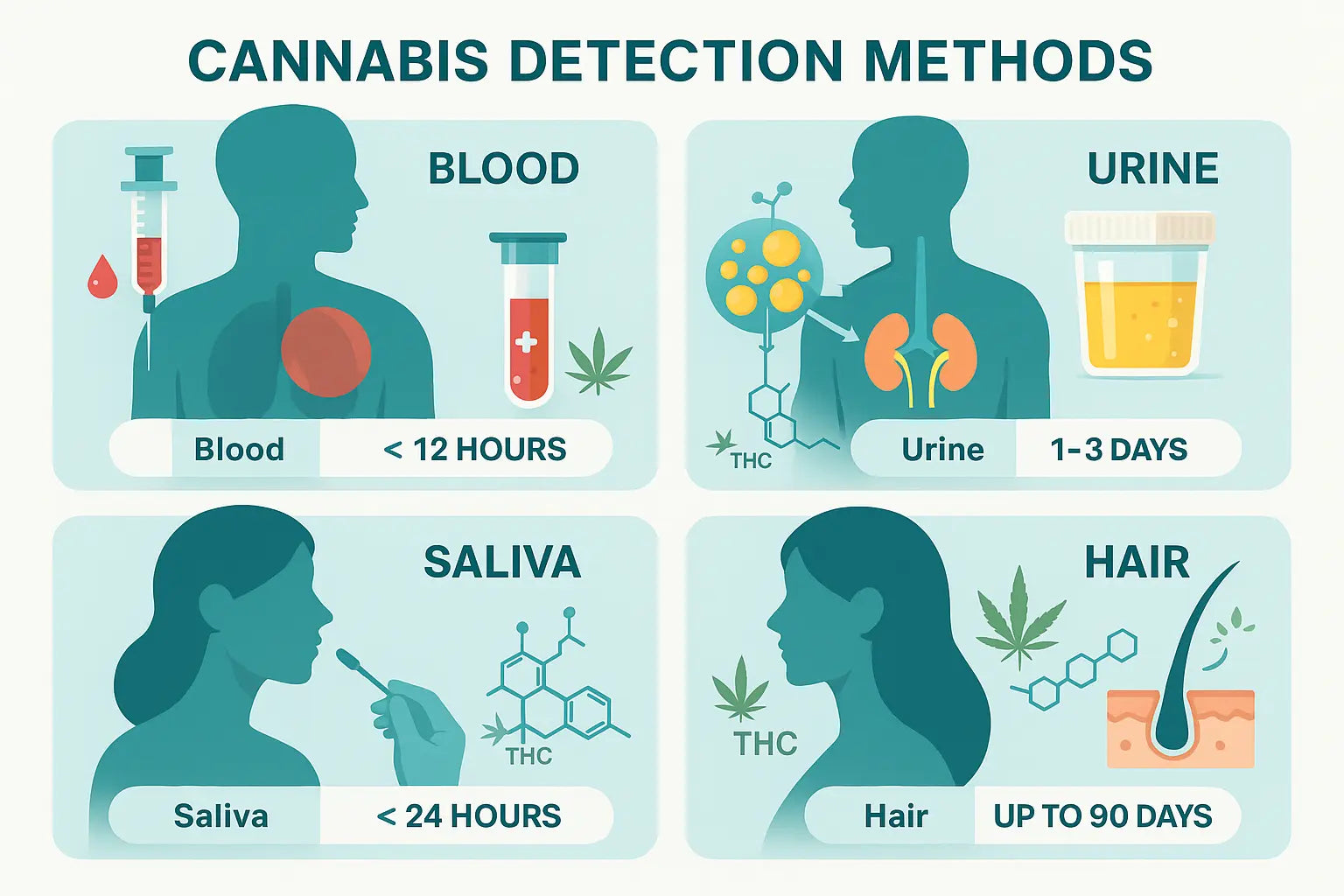
Important Note: Even trace amounts of THC in THCA products can produce psychoactive effects or lead to a failed drug test, especially if the product is exposed to heat or poor storage.
Potency and Effects Variation
Not all cannabis products hit the same way. Potency depends on multiple factors related to the cannabis plant and how it is processed.
What affects potency:
-
Genetics of the strain: Different cannabis strains naturally produce more THCA or THC
-
Harvest timing: Harvesting too early or too late affects the cannabinoid profile
-
Curing and processing methods: Influence how much THCA converts into THC
Products with high THCA content only produce intoxicating effects if heated. If left in its raw form, the product stays non psychoactive and may support brain function, immune health, and inflammation control.
This variability is why labeling matters and why cannabis enthusiasts should always review the product’s chemical composition before consuming cannabis for wellness or chronic pain.
Drug test concerns also increase with higher THC levels, especially for users subject to workplace screening. If you are asking, "Is THCA the same as THC?" just know their usage, activation, and effects are entirely different.
Safety, Legality, and Labeling
THCA is legal in some regions if derived from hemp that contains less than 0.3% THC. However, since it can convert THCA into THC, legal status is tricky. Some regulators classify it based on its potential to produce intoxicating effects.
For example, in the United States, the 2018 Farm Bill allows the sale of hemp-derived THCA products only if the product does not exceed 0.3% THC by dry weight. However, states like Idaho and Kansas do not distinguish between THCA and THC, meaning thca products are still restricted. This inconsistency adds confusion for cannabis consumers across state lines.
Always check local laws before purchasing THCA products. The controlled substance status can vary depending on your state or country.
Drug Testing Implications
Drug testing is a serious consideration for anyone using cannabis products, especially in workplaces with zero-tolerance policies.
-
Even if a product is labeled as non psychoactive or contains tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA), heating it produces THC and may lead to a failed drug test.
-
THC metabolites can remain in the body for days or weeks, depending on frequency of use, dosage, and body composition.
-
THCA flower, if smoked or exposed to high heat during storage, may partially convert into THC and show up on screenings.
-
Some raw food supplement formats containing THCA could still pose a testing risk due to trace THC or unintentional decarboxylation.
In short, consuming cannabis in any form may carry risk for drug testing, even if the product is advertised as non psychoactive.
Responsible Use and Medical Guidance
Before adding any cannabis products into your wellness routine, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider. This is especially true for individuals managing chronic pain, anxiety, or neurodegenerative diseases.
-
THCA and THC can interact with other medications, such as blood thinners or SSRIs
-
THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system, impacting sleep, mood, and appetite
-
Patients with cardiovascular or psychiatric conditions should be extra cautious
-
Starting with low doses of non psychoactive cannabinoids can help minimize unwanted euphoric effects
Responsible use also means keeping track of how your body reacts to different cannabis strains and products. What works for one person may not work for another.
Importance of Accurate Labeling
Labels should always specify whether a product contains tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA), activated THC, or both. This helps cannabis consumers:
-
Understand the difference between psychoactive and non psychoactive compounds
-
Choose products that align with personal tolerance, needs, or medical concerns
-
Avoid unexpected euphoric effects or intoxicating results
What to look for on labels:
-
"THCA content: XX%"
-
"Contains raw cannabis"
-
"Not decarboxylated"
-
"May produce psychoactive effects if heated"
For example, a tincture labeled as containing 25mg of tetrahydrocannabinol acid per serving but with no heat exposure is likely to be non psychoactive. But if baked into edibles, that same tincture produces THC and may cause euphoric effects.
Whether you are looking for a gentle daytime aid or trying to avoid a failed drug test, knowing how your cannabis was processed matters. Accurate labeling supports safer, smarter, and more satisfying experiences.
Final Words
When it comes to thca vs thc, the right choice depends on your goals.
-
Choose THCA if you want potential therapeutic properties like anti inflammatory or neuroprotective effects without getting high.
-
Choose THC if you're looking for relief from chronic pain, nausea, or need help with appetite stimulation.
Understanding the difference between these two compounds helps you use the cannabis plant more intentionally. Whether you prefer raw form, thca flower, or activated cannabis products, being informed leads to better outcomes.
Here at Mary Go Round, we believe smart cannabis use starts with knowledge. Want to learn more about how cannabinoids affect your body and your sesh? Keep exploring our blog or shop our top-rated cannabis accessories!
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have burning questions, we at Mary Go Round are happy to help!
Does THCA Give a High?
No, THCA does not give a high. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw cannabis. It does not produce euphoric effects because it does not activate the brain's cannabinoid receptors the way THC does. So, consuming THCA will not result in intoxication.
Does Smoking THCA Convert It to THC?
Yes, smoking THCA converts it to THC. When THCA is exposed to heat, it undergoes decarboxylation and becomes THC. This process activates the psychoactive compound that causes euphoric effects. So, smoking or vaping THCA-rich products will produce THC.
Why Is THCA Legal but Not THC?
THCA is legal in many places because it is non psychoactive and does not produce intoxicating effects. THC is classified as a controlled substance due to its psychoactive properties. The legal status of THCA can change if it is heated and converted into THC. Always check your local laws before buying or consuming THCA products.