THC vs THCA: Key Differences and Benefits Explained
Posted by Tom Wittneben on
Searching for THC vs THCA to understand their differences? Here’s the quick answer: THC is psychoactive and gets you high, while THCA is non-psychoactive and found in raw cannabis. This article will help you understand their unique effects, benefits, and how to choose based on your needs.
Key Takeaways
-
THCA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that does not produce a high, whereas THC is psychoactive and responsible for the intoxication associated with cannabis use.
-
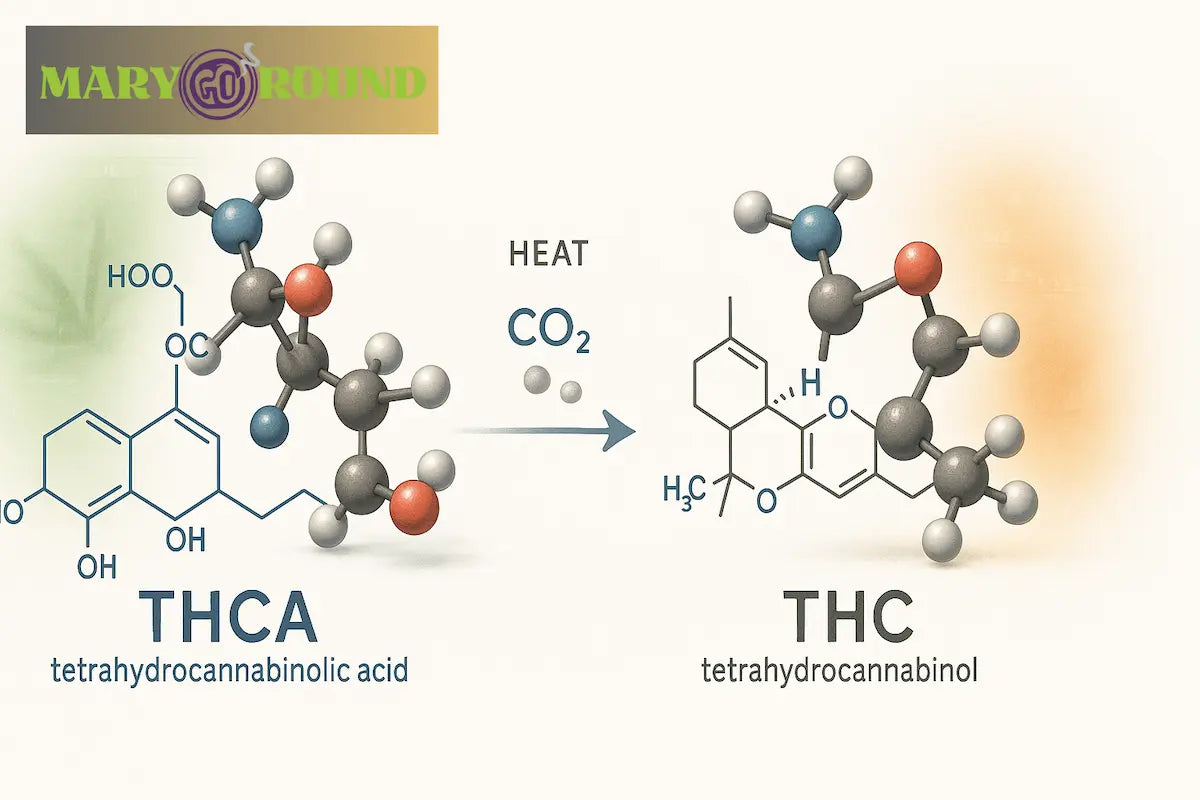
The conversion of THCA to THC occurs through a process called decarboxylation, which happens when cannabis is heated, activating THC’s psychoactive properties.
-
Both cannabinoids offer distinct therapeutic benefits; THCA is known for anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties without psychoactivity, while THC is effective for pain relief and appetite stimulation.
Understanding THC and THCA
THCA and THC are naturally occurring cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. While they share a common origin, their effects on the human body are markedly different. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is non-psychoactive and does not produce a high. On the other hand, THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound responsible for the intoxicating effects often associated with cannabis use.
Knowing the differences between THCA and THC helps in making informed decisions about cannabis consumption. Whether you’re consuming raw cannabis or using different cannabis products, knowing how these cannabinoids interact with your body can help you achieve the desired effects while minimizing unwanted side effects.
Your individual goals and lifestyle preferences should guide your choice between using THCA and THC, especially when considering thca vs thc.
What is THCA?
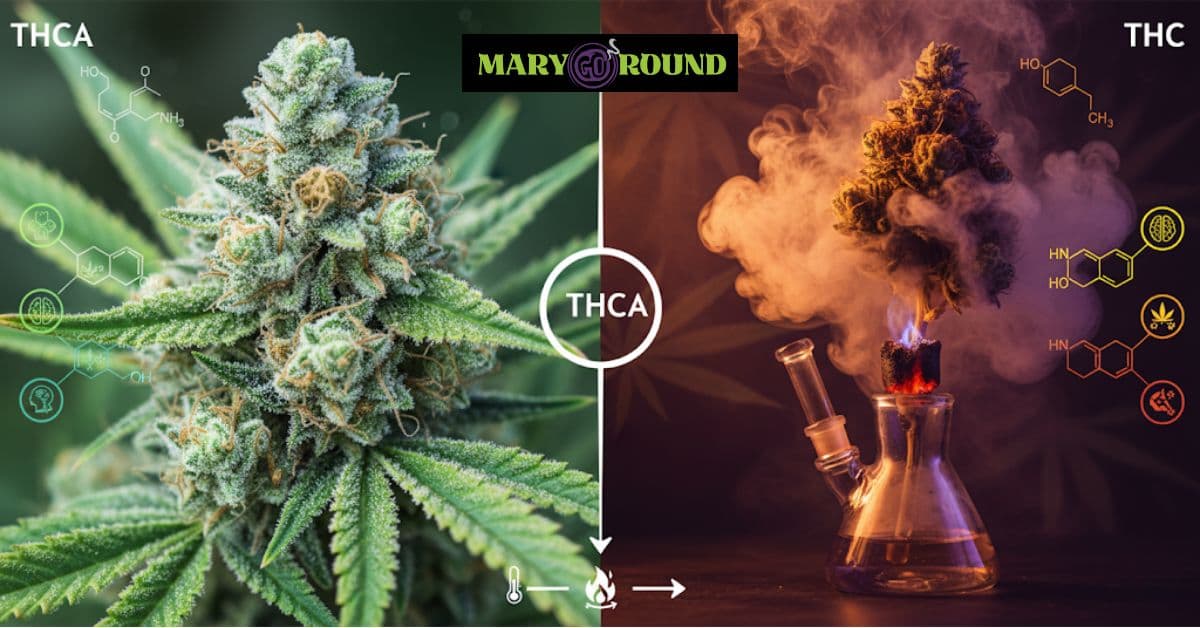
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. It is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is present in raw cannabis. Unlike THC, THCA does not bind effectively to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which is why it does not produce a high. This naturally occurring cannabinoid is commonly present in freshly harvested cannabis plants and remains in its non-psychoactive form until it undergoes a heating process known as decarboxylation.
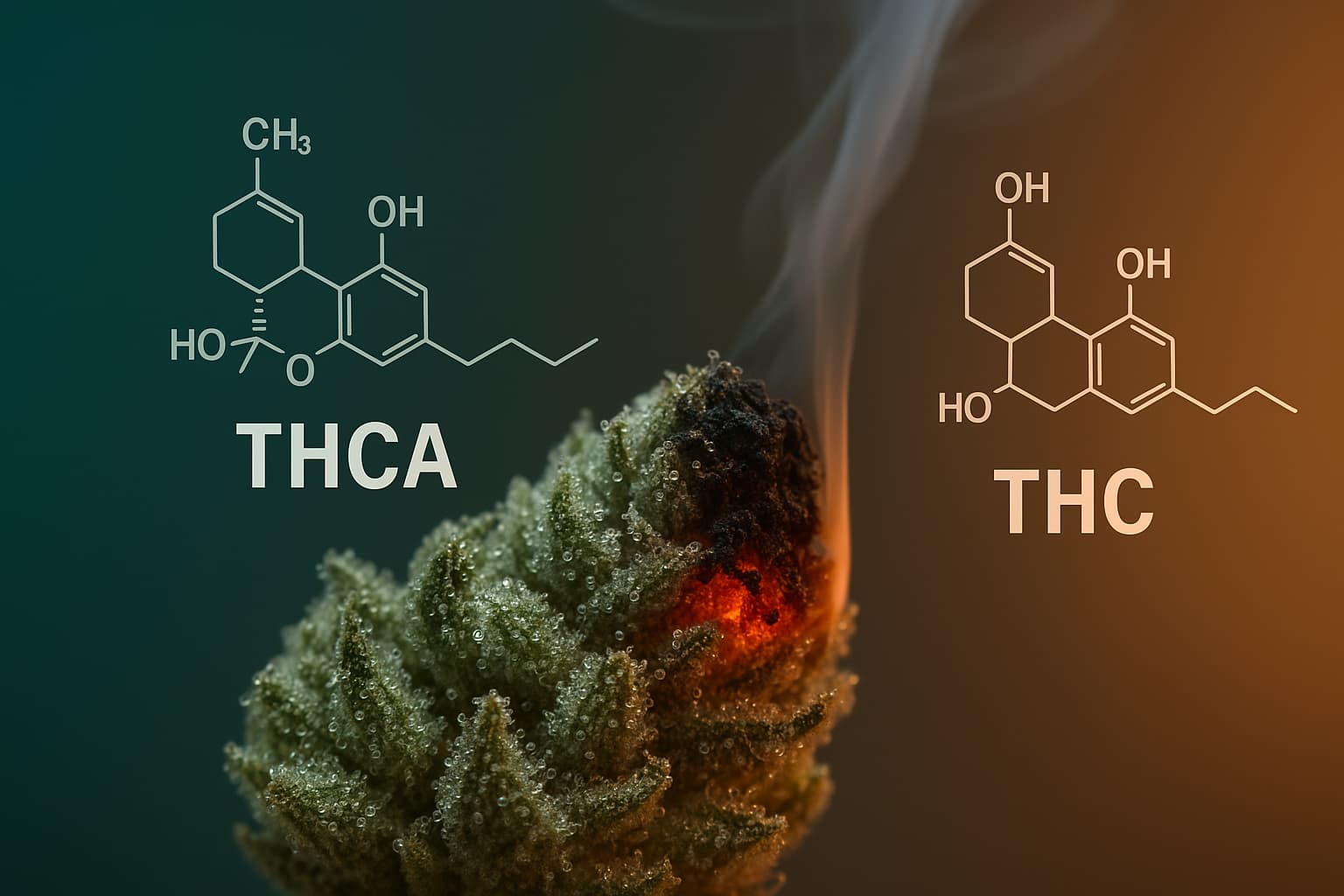
The chemical structure of THCA includes an additional carboxyl group, distinguishing it from THC. This carboxyl group is responsible for the non-psychoactive properties of THCA, making it a preferred choice for individuals seeking the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the intoxicating effects of THC.
What is THC?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis responsible for the intoxicating effects users experience. This cannabinoid interacts with the brain’s CB1 receptors, leading to altered perception, euphoria, and relaxation. THC is widely recognized for its recreational and medical uses, making it a popular component of various cannabis products.
Derived from the decarboxylation of THCA, THC is found in higher concentrations in dried and cured cannabis plants. The effects of consuming THC can vary significantly based on dosage, method of consumption, and individual tolerance levels. As a result, THC has become a central focus for both recreational users and medical cannabis patients.
Chemical Composition and Conversion Process
The chemical composition of THCA and THC plays a crucial role in their differing effects. THCA, found in raw cannabis plants, is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC. This difference in chemical structure is due to the presence of an additional carboxyl group in THCA, making it a larger and non-psychoactive molecule.
This carboxyl group is removed through a chemical reaction called decarboxylation, which occurs when cannabis is heated. This process converts THCA into THC, activating its psychoactive properties. Understanding this conversion is essential for effectively utilizing cannabis consumption methods and achieving the desired effects. Curious about how heat transforms THCA into psychoactive THC? We break down the process and what to expect when smoking.
Structural Differences
THCA and THC differ primarily in their chemical structure. THCA has an extra carboxyl group, making it a larger molecule. This carboxyl group is the reason THCA does not bind well to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, preventing it from inducing a high. The presence of this carboxyl group is what makes THCA non-psychoactive.
In contrast, THC lacks this group, allowing it to interact effectively with CB1 receptors and produce psychoactive effects. Understanding these key structural differences is essential for recognizing how each cannabinoid functions within the body.
Decarboxylation Process
Decarboxylation is the chemical reaction that converts THCA into THC when cannabis is exposed to heat. This process is crucial for activating the psychoactive properties of cannabis, as THCA remains non-psychoactive until it undergoes decarboxylation.
Factors such as temperature, duration of heating, and the use of a vacuum can affect the efficiency of decarboxylation. For effective decarboxylation, it is recommended to use a temperature range of 230-250 degrees Fahrenheit. The process should last for 30-40 minutes. This process ensures that THCA loses its carboxyl group and transforms into psychoactive THC, leading to the desired effects.
Psychoactive Properties of THC vs Non-Psychoactive THCA
THC and THCA have distinct psychoactive properties due to their chemical structures. THC is known for its ability to induce psychoactive effects, such as altered perception and euphoria. This is due to THC’s interaction with CB1 receptors in the brain, making it the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis.
In contrast, THCA is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC found in raw cannabis plants. THCA does not produce a high but may offer similar therapeutic effects as THC without the intoxicating effects. This makes THCA an attractive option for those seeking the health benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive effects. If you're curious about the potency and psychoactive effects of THCP compared to THCA, check out our detailed comparison.
THC's Psychoactive Effects
THC produces its psychoactive effects by how THC interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain. This interaction can lead to altered perception, mood changes, and feelings of euphoria. Many users experience relaxation and altered sensory perceptions, making THC a popular choice for recreational marijuana use.
High doses of THC may lead to side effects. These can include anxiety, paranoia, impaired memory, and coordination issues. The impact of THC can vary significantly among individuals based on factors like tolerance and dosage, highlighting the importance of responsible consumption.
THCA's Non-Psychoactive Benefits
THCA offers several non-psychoactive benefits, making it an appealing option for therapeutic use. Unlike THC, THCA does not produce a high because it does not bind effectively to cannabinoid receptors in the brain. This allows for the use of THCA without the intoxicating effects associated with THC.
THCA may help reduce inflammation and offer neuroprotective benefits. These properties make THCA beneficial for managing conditions like arthritis and inflammatory disorders. Its non-psychoactive nature also allows for daily use without impairing cognitive functions, providing a balanced approach to cannabis consumption.
Potential Therapeutic Benefits of THCA and THC
Both THCA and THC offer unique therapeutic benefits, catering to different medical needs. THCA is known for its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis and chronic pain without causing intoxicating effects. This allows users to experience relief and improved quality of life without the psychoactive effects of THC.
THC, on the other hand, is associated with several therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and reducing nausea. These properties are highly valuable for patients undergoing treatments for conditions like cancer, where THC can help manage pain and improve appetite. Explore the therapeutic benefits of THCA compared to Delta 8 in our in-depth cannabinoid guide.
Both cannabinoids present unique therapeutic profiles, enabling tailored approaches to medical cannabis use.
THCA's Health Benefits
THCA is commonly consumed through raw cannabis products like juices and tinctures, offering significant health benefits without the high. It has potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, making it beneficial for managing conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and neurodegenerative diseases.
THCA’s benefits also include anti nausea properties and antioxidant properties, contributing to overall wellness and potential health benefits. Its non-psychoactive nature allows for therapeutic use without the intoxicating effects of THC, making it a preferred choice for those seeking health benefits without a high.
THC's Medical Uses
THC is effective for managing chronic and severe pain, providing significant therapeutic value. It is widely used to stimulate appetite, especially in patients undergoing chemotherapy, where it helps manage appetite loss and nausea. For a closer look at how cannabis use may impact body weight and metabolism, see our detailed analysis.
THC also improves sleep quality and can be beneficial for managing anxiety and mood disorders. The metabolism of THC in edibles can result in a stronger and longer-lasting high compared to other methods, providing extended relief for medical conditions.
Consumption Methods for THCA and THC
There are various methods for consuming THCA and THC, each offering different experiences and therapeutic effects. Common methods include inhalation, edibles, and topicals. These methods can significantly alter the intensity and duration of the effects, allowing users to choose the best method for their needs. For readers considering inhalation, our guide on Is THCA safe to smoke and what to consider covers health and safety tips.
THCA is often consumed in raw form through products like flower and tinctures, providing wellness benefits without the high. In contrast, THC can be consumed through products such as THC-infused gummies and pre-rolls, offering psychoactive effects.
Inhalation
Inhalation is a common method of consuming cannabis, primarily through smoking or vaporizing. This method decarboxylates THCA into THC, making it psychoactive and allowing users to feel effects almost immediately due to rapid absorption into the bloodstream. Many people choose to consume cannabis in this way for its efficiency.
However, inhaling cannabis can pose health risks, including potential damage to lung health from smoking and uncertain effects from vaping. Despite these risks, inhalation tends to produce more intense but shorter-lived effects compared to other consumption methods.
Edibles
Edibles are a popular method for consuming THC and THCA, often found in food or drink infused with cannabinoids. This method provides a longer-lasting, slower-onset experience compared to inhalation. The effects of edibles can last longer and often feel stronger, making them a preferred choice for those seeking extended relief.
For those looking to retain the non-psychoactive properties of THCA, it’s important to ensure the product is not heated. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it is recommended to find the right amount and avoid unexpected effects. THCA capsules, for instance, can be used as a daily supplement for non-psychoactive therapeutic benefits.
Topicals and Sublinguals
Topicals infused with cannabinoids provide targeted relief for sore muscles or achy joints without causing psychoactive effects, as they do not enter the bloodstream. These products are ideal for localized pain relief and inflammation, allowing users to experience the therapeutic benefits of THCA and THC without the high.
Sublingual consumption involves placing drops or tinctures under the tongue, allowing for rapid absorption into the bloodstream. This method provides a controlled dose and can be adjusted gradually to manage the effects better.
Topicals and sublinguals offer versatile options for cannabis consumption, catering to different therapeutic needs.
Legal Status and Implications
The legal status of THC and THCA is not uniform. It changes significantly based on local laws and regulations. THC remains classified as a Schedule I substance in the United States, indicating it has no accepted medical use federally, although it is legal for medical and/or recreational use in some regions. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, with some countries moving towards decriminalization or legalization.
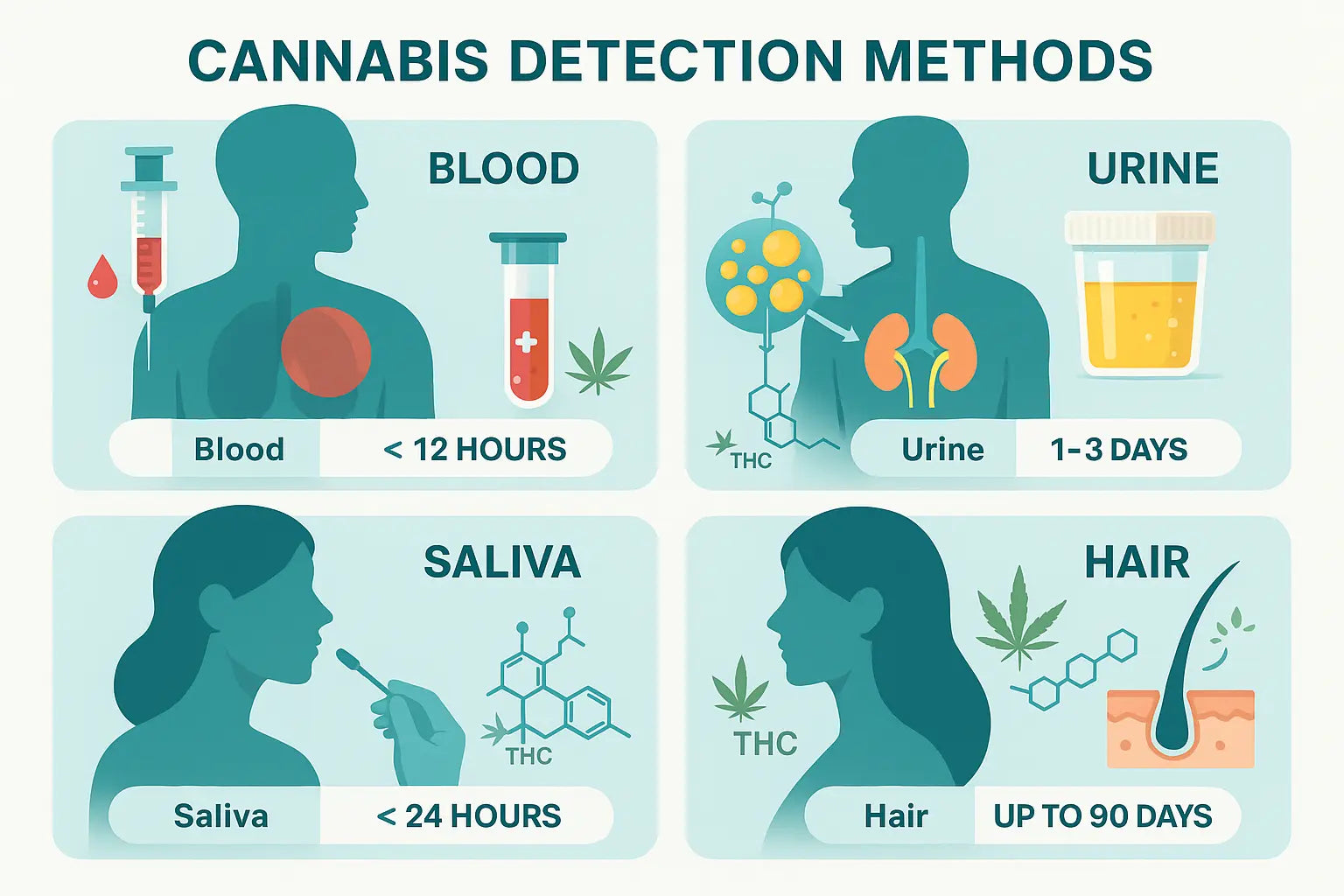
THCA’s legal status can be more ambiguous. Despite its non-psychoactive nature, THCA detection in drug testing can be complex due to varying state regulations and workplace policies. The legality of THCA often depends on its association with THC and the specific definitions used in local laws. Sellers of THCA-rich products should be aware of possible legal pitfalls and stay informed about regulatory changes.
THC Legality
THC is classified as a Schedule I substance under U.S. federal law, indicating it is considered to have no accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. However, the legal status of THC varies significantly by region, with some states and countries legalizing it for medical or recreational use. It’s important to check local cannabis laws to ensure compliance, as the regulations can differ dramatically.
The 2018 Farm Bill created a loophole, differentiating hemp-derived cannabinoids from THC, leading to differing interpretations of legality. This has allowed for the sale of certain THC products in some regions while remaining illegal in others, creating a complex legal landscape for consumers and sellers alike.
THCA Legality
THCA is legally allowed in its natural state with less than 0.3% delta-9 THC. However, its legality can vary significantly by state and can be less clear than its status at the federal level. The legal framework significantly influences THCA’s availability and use, with some states allowing its use while others impose restrictions.
Sellers of THCA-rich products should be aware of possible legal pitfalls, as THCA can be subject to varying interpretations of legality. Despite its non-psychoactive nature, THCA’s association with THC can complicate its legal status, requiring careful consideration of local laws and regulations.
Managing THC Dependence and Withdrawal Symptoms
THC dependence is a potential risk for regular users, influenced by factors such as genetic predisposition and frequency of use. Managing THC withdrawal involves addressing cravings, anxiety, and gastrointestinal issues, which can arise when reducing or stopping THC consumption. Understanding the risks and recognizing the signs of dependence are crucial for maintaining a healthy relationship with cannabis.
Professional treatment options for THC dependence include cognitive-behavioral therapy and support groups, which provide tools and support for overcoming addiction. These therapies can help individuals manage withdrawal symptoms and address the psychological aspects of dependence. Detoxification programs may also be recommended for those with severe THC dependency.
Risks of THC Dependence
Regular use of THC may contribute to cognitive decline and mental health issues, particularly among younger individuals. THC can impair memory, coordination, and judgment, leading to potential health risks. Frequent and heavy use raises the risk of developing dependence, with approximately 30% of marijuana users potentially developing a disorder with regular THC use.
The risk of THC dependence increases with chronic use, potentially leading to withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, insomnia, and cravings. Individuals facing mental health challenges should consult a professional before using THC to avoid exacerbating any underlying issues. If concerned about THC dependence, seeking professional advice is recommended.
Treatment Options
Professional treatment for THC addiction may include cognitive-behavioral therapy and support groups, which facilitate the provision of support and tools for overcoming addiction. These therapies help individuals develop coping strategies and manage withdrawal symptoms effectively.
Detoxification programs are often recommended for individuals with severe THC dependency. Many treatment options for THC dependence are covered by insurance, making them accessible to those in need. Seeking professional help is crucial for managing THC dependence and achieving long-term recovery.
THC vs THCA Wrapped
In summary, understanding the key differences between THC and THCA is essential for making informed decisions about cannabis use. THCA, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw cannabis, offers numerous therapeutic benefits without the intoxicating effects of THC. On the other hand, THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, provides significant medical value, particularly for pain relief, appetite stimulation, and reducing nausea.
Both cannabinoids present unique therapeutic profiles that cater to different medical needs. By exploring various consumption methods and staying informed about the legal status and potential risks of THC dependence, users can make the most of the therapeutic benefits these cannabinoids offer. Whether you’re seeking the psychoactive effects of THC or the wellness benefits of THCA, understanding their properties and applications will enhance your cannabis experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between THC and THCA?
The main difference is that THC is psychoactive and induces a high, whereas THCA is non-psychoactive and does not produce such effects.
How does decarboxylation affect THCA?
Decarboxylation converts THCA into THC by removing a carboxyl group, which activates its psychoactive properties. Therefore, this process is essential for achieving the effects typically associated with cannabis consumption.
What are the therapeutic benefits of THCA?
THCA provides therapeutic benefits such as anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea effects, which can aid in managing conditions like arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
Is THC legal everywhere?
THC is not legal everywhere; its legality varies significantly across different regions, being classified as a Schedule I substance in the U.S. but permitted for medical or recreational use in certain states and countries.
How can THC dependence be managed?
THC dependence can be effectively managed with cognitive-behavioral therapy, participation in support groups, and detoxification programs; seeking professional treatment is crucial for successful recovery.