THCP vs THCA: Key Differences and Benefits Explained
Posted by Tom Wittneben on
Ever wondered what the next big thing in cannabis might be? While THC has long reigned as the most talked-about cannabinoid, its lesser-known relatives are stepping into the spotlight, each with unique characteristics and potential.
Here's what most guides won't tell you: These cannabinoids don't just differ, they represent opposing approaches to cannabis consumption. One preserves the plant's original chemistry, while the other pushes potency boundaries science is still trying to understand.
Buckle up. We’re digging deep into the science, the hype, and the real-world stakes of THCA vs. THCP. No jargon, just the crucial intel you need before choosing your side.
What is THCA?
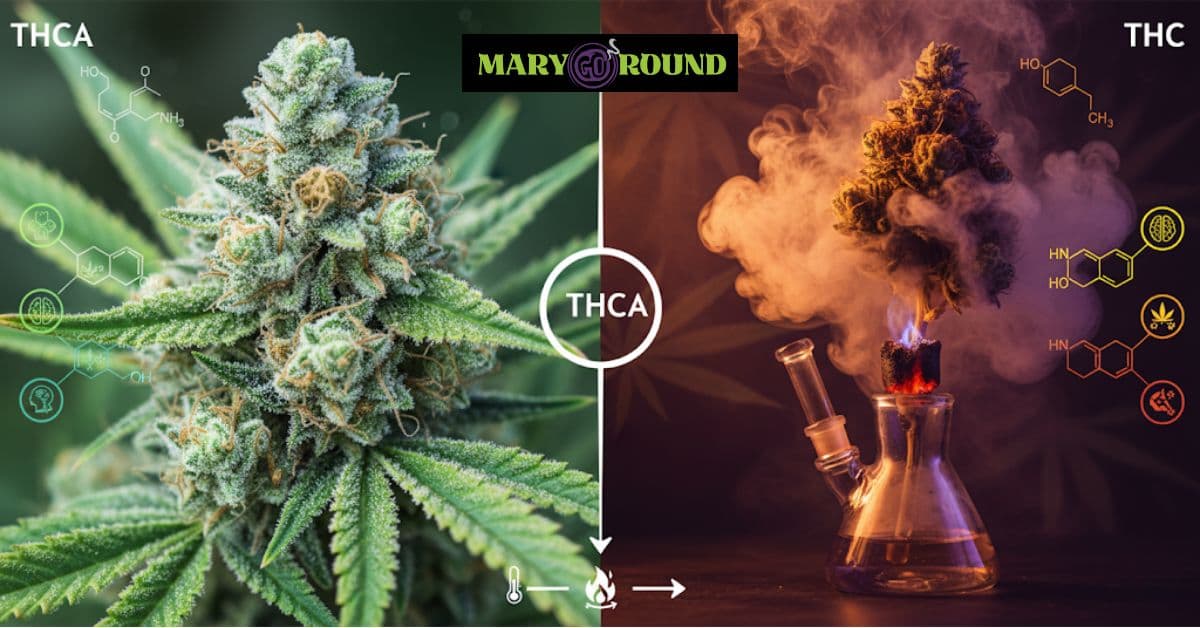
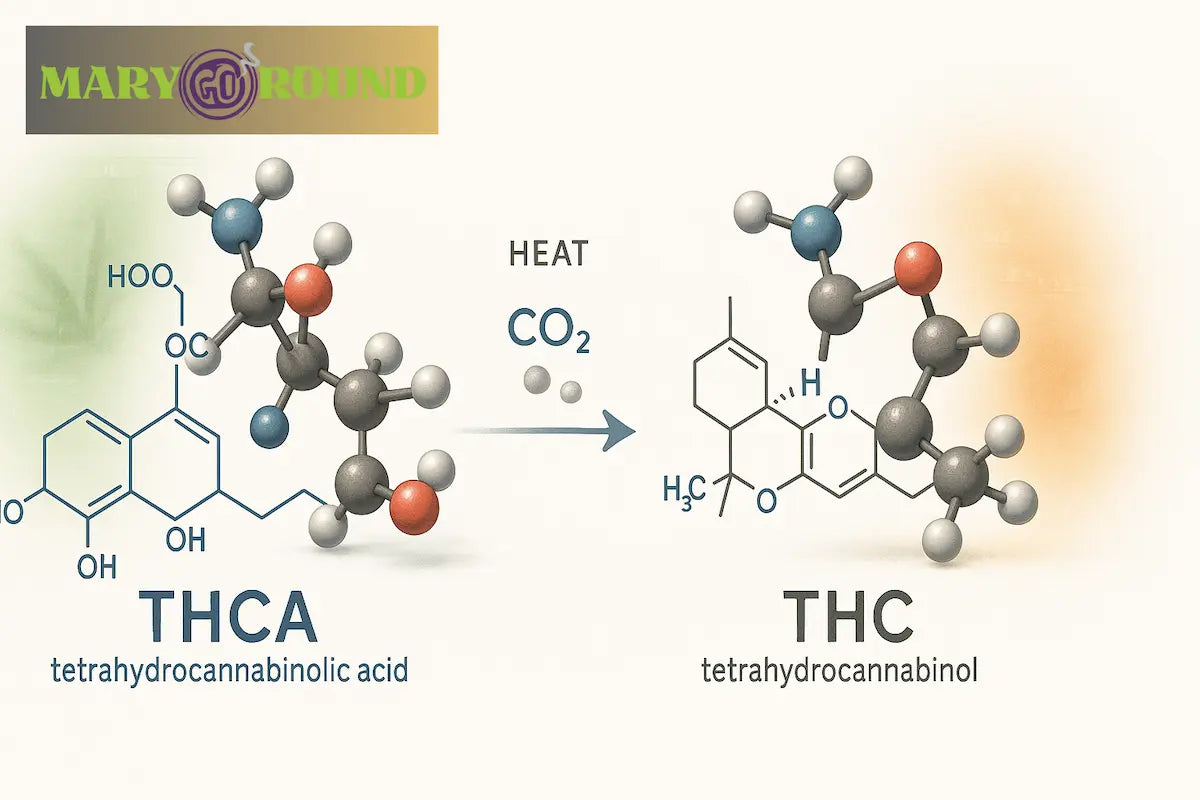
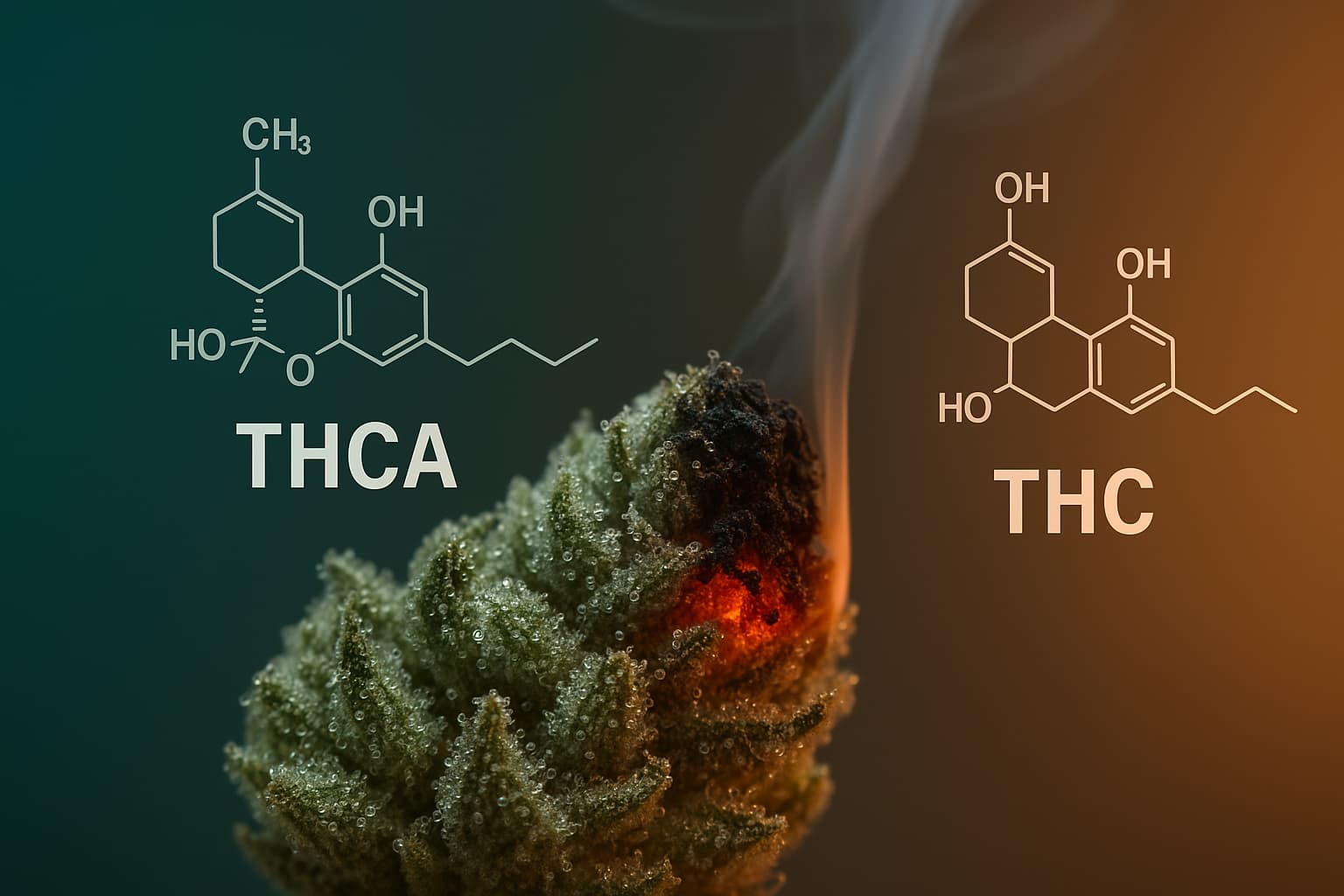
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found abundantly in raw and undried cannabis plants. Think of THCA as the acidic form of THC. As the plant dries and especially when it's heated (through smoking, vaping, or cooking), a process called decarboxylation occurs, converting THCA into the psychoactive THC.
While THCA itself doesn't produce the "high" associated with THC, research suggests it may possess its own therapeutic properties. Early studies have explored its potential as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotectant.
However, it's important to note that most of these studies are preclinical, and more human research is needed to confirm these benefits. You can find THCA in raw cannabis flower, certain tinctures, and some edibles that are specifically formulated to retain THCA content.
What is THCP?
Enter tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP), a relatively recent discovery of cannabinoids, identified in 2019 by a team of Italian researchers. What sets THCP apart, and serves as a bridge to its growing scientific interest, is its apparent high potency.
The key to this potency lies in its chemical structure. Like THC, THCP has a side chain, but THCP's side chain is significantly longer, containing seven carbon atoms compared to THC's five.
According to the researchers who discovered it, this longer alkyl side chain allows THCP to bind more strongly to the CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. These CB1 receptors are primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids. Initial in vitro studies suggested that THCP could bind to CB1 receptors up to 33 times more potently than THC.
This indicates that even small amounts of THCP could potentially produce very strong psychoactive effects.
Psychoactive vs. Non-Psychoactive Effects
THCP: Psychoactive Effects
Users can experience the following psychoactive effects:
-
Euphoria
-
Deep relaxation
-
Altered sensory perception
-
Cognitive impairment
-
Changes in mood and emotional state
These effects are often reported as stronger and longer-lasting than those produced by THC, with some anecdotal reports suggesting effects may last up to 24 hours or more. Negative effects, especially at higher doses, can include anxiety, paranoia, dry mouth, increased heart rate, dizziness, and, in rare cases, psychosis. Because of its potency, even experienced cannabis users may be more susceptible to adverse reactions.
THCP: Non-psychoactive Effects
There is currently no evidence to suggest that THCP has significant non-psychoactive effects, as its main action is through strong activation of CB1 receptors in the brain, which are responsible for intoxication and altered mental states.
THCP: Therapeutic Effects
Although research is in its infancy, early studies suggest that THCP may offer several therapeutic benefits, likely due to its strong interaction with the endocannabinoid system. They include:
-
Pain relief
-
Anti-inflammatory effects
-
Appetite stimulation
-
Potential for lower dosing
However, the heightened potency also means there is a greater risk of adverse effects, and more research is needed to fully understand its safety and efficacy.
THCA: Psychoactive Effects
On its own, THCA does not produce psychoactive effects because it does not effectively bind to CB1 receptors in the brain. Only when THCA is decarboxylated (heated) does it convert to THC, which is psychoactive.
THCA: Non-psychoactive Effects
THCA is classified as a non-psychoactive cannabinoid. It interacts with the body in ways that do not result in intoxication or altered perception. Instead, it may affect other physiological processes through different pathways.
THCA: Therapeutic Effects
Several potential therapeutic uses for THCA includes the following:
-
Anti-inflammatory properties
-
Neuroprotective effects
-
Antiemetic (anti-nausea) effects
-
Anticonvulsant potential
Since individual experiences vary, both THCP and THCA require significantly more research to fully understand their effects, safety profiles, and therapeutic potential.
THCA vs THCP: Key Differences
When comparing THCP and THCA, it's essential to understand that these two cannabinoids offer distinctly different experiences and benefits. THCP is renowned for its extraordinary potency and strong psychoactive effects, making it appealing to those seeking intense euphoria or therapeutic impact at low doses.
In contrast, THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form and is valued primarily for its potential wellness benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, without causing intoxication.
The following table provides a clear side-by-side comparison to help illustrate the key distinctions between THCP and THCA, enabling consumers to make informed choices based on their individual needs and preferences.
|
Feature |
THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) |
THCP (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) |
|
Psychoactivity |
Non-psychoactive in raw form |
Potentially highly psychoactive |
|
Potency |
Low potency in its raw form |
Significantly higher potency than THC |
|
Chemical Structure |
Shorter alkyl side chain (5 carbons) |
Longer alkyl side chain (7 carbons) |
|
CB1 Receptor Binding |
Lower binding affinity |
Significantly higher binding affinity |
|
Abundance in Plant |
Found in high concentrations in raw cannabis |
Found in very low concentrations |
|
Discovery Year |
Long known |
Discovered in 2019 |
Effects and Benefits Compared
The effects and benefits of THCA and THCP are areas of ongoing research.
As mentioned earlier, preclinical studies suggest potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Some users have also reported potential benefits; for example, one Reddit user shared, "I've got some Cannatonic #3 from FlowGardens that's around 10%/10% thc/cbd and it's some of the best hemp I've ever tasted”. Learn about the relationship between cannabis use and body mass index (BMI), including surprising research findings on weight in our in-depth guide.
For THCP, due to its high potency, the effects are likely to be much stronger than THC. Users might experience intense euphoria, altered perception, and increased relaxation. However, because it's a newer discovery, research on its specific therapeutic benefits is limited. It's theorized that it might have similar benefits to THC, but at much lower doses, potentially offering more effective relief for certain conditions. Learn how THCA compares to both THC and THCP for a complete understanding of psychoactive and non-psychoactive options.
Expert Insight: According to Dr. Ethan Russo, a renowned cannabis researcher, “CBD is a versatile anti-inflammatory analgesic through numerous distinct mechanisms, and various other minor cannabinoids and terpenoids in Cannabis certainly may contribute notably to the therapeutic profile of Cannabis. Numerous basic science and even clinical trial data support the concept of herbal synergy in Cannabis beyond the effects of single components. We are only seeing the very beginnings of the therapeutic potential of this plant!”
This statement underscores that the full therapeutic potential of cannabis is still being uncovered.
Safety and Side Effects
THCA is generally considered safe when consumed in its raw, non-decarboxylated form. As a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, it does not produce the "high" associated with THC, as earlier discussed, making it appealing for those seeking therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
Most users tolerate THCA well, but mild side effects have been reported, including gastrointestinal discomfort, dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue, and, in rare cases, cognitive impairment or upset stomach. Importantly, THCA does not bind directly to CB1 receptors, so it does not alter perception or mood.
However, THCA can convert to THC if exposed to heat (through smoking, vaping, or cooking), which can then produce psychoactive effects and increase the risk of intoxication or impairment. For this reason, individuals who are sensitive to THC or wish to avoid psychoactive effects should be mindful of how they consume THCA products.
THCA is considered non-addictive and has a low risk of dependence. Still, certain groups, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, people with heart conditions, or those with cannabinoid sensitivities, should consult a healthcare provider before use. As with any supplement, responsible dosing, product quality, and medical guidance are important for minimizing risks. Learn about the mango effect and cannabis synergy—how eating mangoes may amplify or alter your high.
On the other hand, THCP is a much more potent cannabinoid, binding to CB1 receptors with far greater affinity than THC. Because of this, even small doses can produce strong psychoactive effects, including euphoria, altered perception, and deep relaxation.
However, the increased potency also raises the risk of side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, dizziness, rapid heart rate, and, in some cases, psychosis, especially for those with low THC tolerance or a predisposition to mental health conditions. Due to limited research on THCP, its full safety profile is not yet known, but caution is strongly advised when trying this compound, particularly for new or sensitive users.
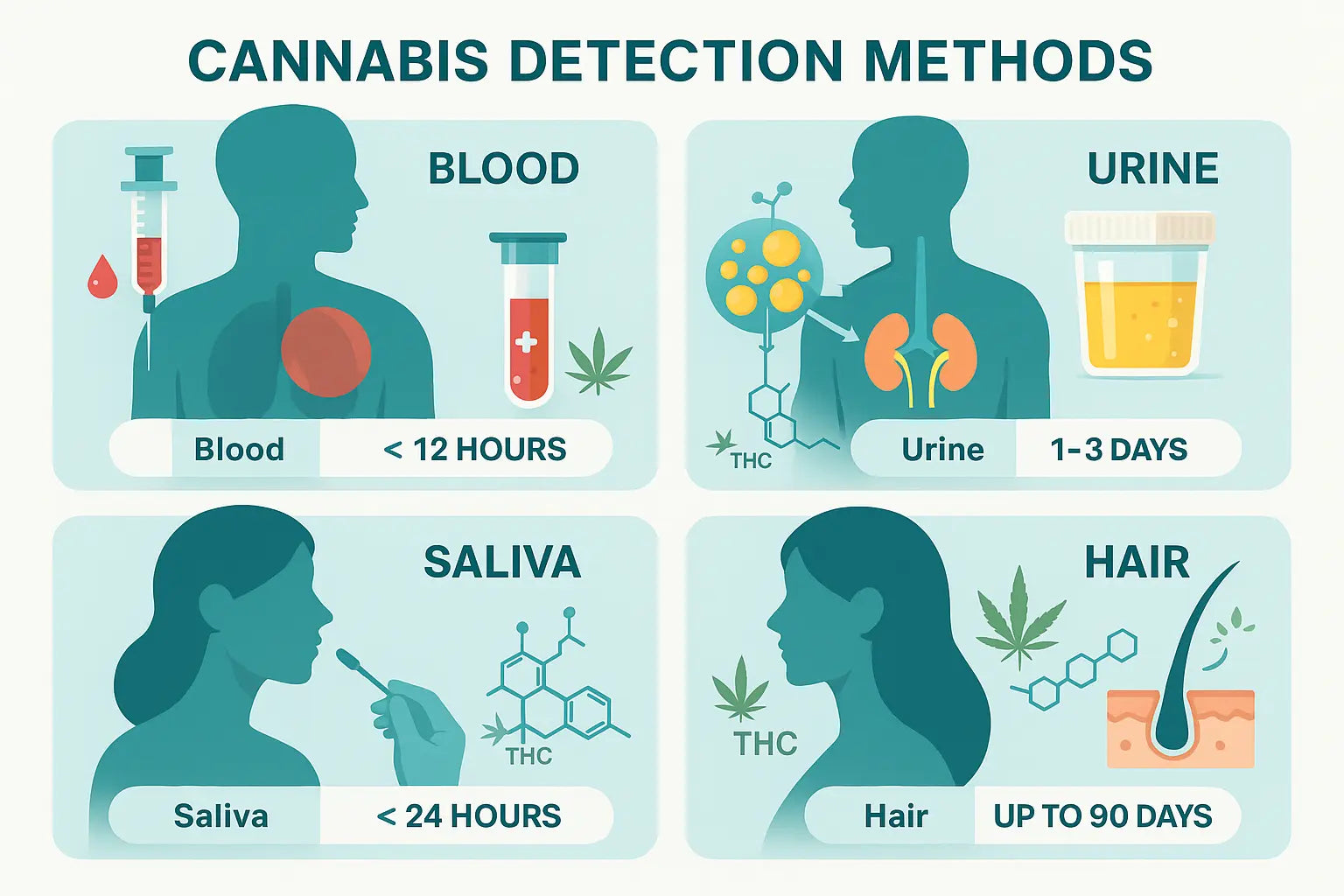
Drug Testing Risks
Both THCA and THCP may trigger positive results on drug tests designed to detect THC metabolites. While THCA itself is not psychoactive, it can decarboxylate into THC in the body or during sample handling, potentially resulting in a positive test. For a breakdown on how long THCA stays in your system and drug testing risks, see our definitive guide.
THCP, due to its structural similarity to THC, is also likely to be metabolized in ways that standard drug tests can detect. Anyone subject to workplace or legal drug testing should be aware of these risks before using products containing THCA or THCP. Compare the differences in how long THCA and Delta 8 stay in your system for smarter choices about cannabinoid use and drug testing in our guide
All in all, choosing reputable, lab-tested products and consulting healthcare professionals can help ensure safe and effective use of these cannabinoids.
Legal Status of THCA and THCP
The legal status of THCA and THCP is complex and varies depending on federal and state regulations.
Federal Level: Under the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp-derived cannabinoids containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC are federally legal. THCA in its raw form technically falls under this definition as it is not delta-9 THC.
However, the legal interpretation can be nuanced, especially considering that THCA converts to THC. THCP's legal status is even less clear at the federal level as regulations primarily focus on delta-9 THC content.
State Level: State laws vary significantly. Some states treat all cannabis compounds similarly, while others have specific regulations regarding different cannabinoids. It's essential to check your local state laws regarding the legality of both THCA and THCP.
Above all, always prioritize understanding the specific laws in your region before purchasing or using THCA or THCP products, as its derivatives are constantly evolving.
Best Ways to Use THCA and THCP
In the following points, we’ll explore some of the most effective and popular ways to use these cannabinoids based on their unique properties.
THCA
-
Raw Flower: Consuming raw cannabis (e.g., in smoothies or juiced) allows you to benefit from THCA without psychoactive effects.
-
THCA Diamonds: These are crystalline structures of pure THCA, which can be dabbed or vaporized after decarboxylation for a potent THC experience, or consumed in their raw form for non-psychoactive benefits.
-
THCA Tinctures and Capsules: These offer a convenient and measured way to consume THCA without heating.
THCP
-
Flower Infused with THCP: Due to THCP's low natural abundance, some products involve infusing hemp flowers with THCP extracts.
-
THCP Vapes and Concentrates: These methods allow for the direct consumption of THCP.
-
THCP Edibles: Similar to THC edibles, these can have delayed and intense effects.
Go-To Brands
When exploring THCA and THCP products, it’s important to choose trusted brands that prioritize quality, safety, and transparency. Look for companies that provide third-party lab testing, clear cannabinoid profiles, and responsibly sourced ingredients to ensure you’re getting authentic and effective products.
Some reputable brands known for their commitment to cannabinoid purity and innovation include:
-
Bluebird Botanicals: Renowned for their high-quality hemp extracts and a wide range of cannabinoid products, Bluebird offers carefully formulated tinctures and concentrates that emphasize transparency and consistency.
-
Joy Organics: Known for their broad-spectrum hemp products, Joy Organics provides THC-free and low-THC options with rigorous third-party testing, making them a solid choice for those interested in non-psychoactive cannabinoids like THCA.
-
CBDistillery: A well-established brand offering a variety of hemp-derived cannabinoid products, including isolates and full-spectrum extracts, with clear lab reports and competitive pricing.
-
Kush Queen: Specializing in wellness-focused cannabis products, Kush Queen offers thoughtfully crafted formulations that highlight minor cannabinoids and terpenes, ideal for those seeking targeted therapeutic effects.
By prioritizing these qualities, you empower yourself to make informed decisions and enjoy the unique benefits these cannabinoids offer with confidence.
Choosing Between THCA and THCP
The choice between THCA and THCP depends entirely on your desired experience and preferences.
Choose THCA if:
-
You want to explore the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids without psychoactive effects.
-
You prefer to consume cannabis in its raw form.
-
You are sensitive to THC or want to avoid its intoxicating effects.
Choose THCP (with extreme caution) if:
-
You have a high tolerance for THC and are seeking a significantly more potent experience.
-
You are experienced with cannabis concentrates and understand the importance of micro-dosing.
-
You are in a legal jurisdiction where high-potency cannabis products are permitted and you understand the risks involved.
Whichever path you take, stay informed, start low, and always prioritize your safety for the best possible cannabinoid experience.
Wrapping Up THCP vs THCA
So, THCA or THCP, which will you rather go for? Both could be worth the try, you just need to brace yourself for the ride.
No matter which you choose, remember to prioritize education, start low and go slow, and always respect the power of these compounds. This is how the best experiences start.
And hey, if you’re looking for trusted ways to enjoy these cannabinoids, swing by Mary Go Round, we’ve got your back with top-notch gear for every kind of journey. Want to try?
Upgrade Now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is THCP stronger than THCA?
Yes, THCP is significantly stronger than THCA. THCP is a potent psychoactive cannabinoid that binds more effectively to cannabinoid receptors, resulting in intense psychoactive effects, whereas THCA is non-psychoactive and does not induce a high.
Will THCP get you high?
Absolutely! THCP will get you high due to its potent psychoactive effects, making it a preferred choice for those seeking a traditional cannabis high with heightened intensity.
What do THCA and THCP do together?
When combined, THCA and THCP can offer a balanced experience. THCA provides therapeutic benefits without psychoactive effects, while THCP delivers intense euphoria.
What is better than THCA?
For those seeking non-psychoactive benefits, THCA is excellent due to its therapeutic properties. However, if potent psychoactive effects are desired, THCP or other cannabinoids like delta-9 THC may be preferred for their ability to induce a traditional cannabis high.